# Introduction
# What is Python?
PrePython: Lesson 1 - Introduction (opens new window)
# Control Flow
There are only 3 statements for using in every algorithm. On the other hand, it means every program or algorithm is combination of only 3 statements.
To emphasize, Only those statements can solve any problem in term of creating algorithm in Computer Science.
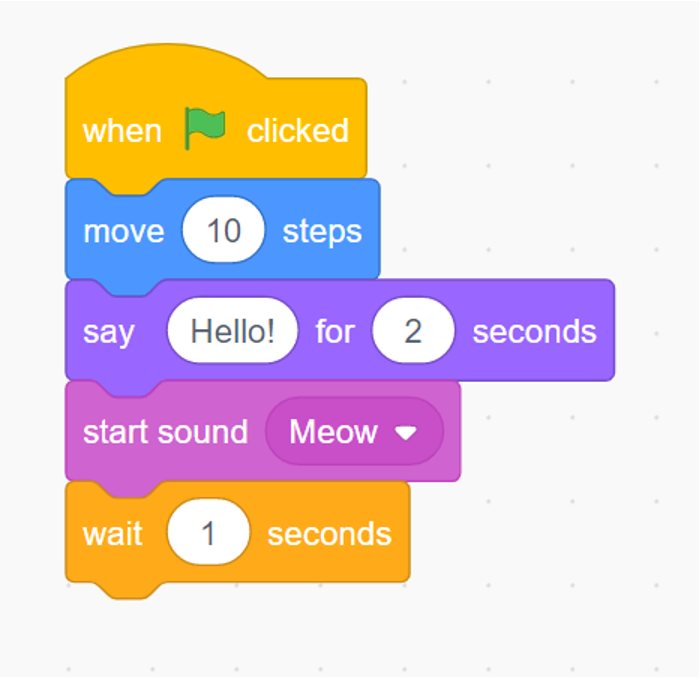
# Sequence
Sequence is talking about the ordered of the code. The code must be read on the ordered sequencing of successive commands.
For example, Top-to-Bottom, Left-to-Right or Right-to-Left (based on Operator Precedence)
# Condition
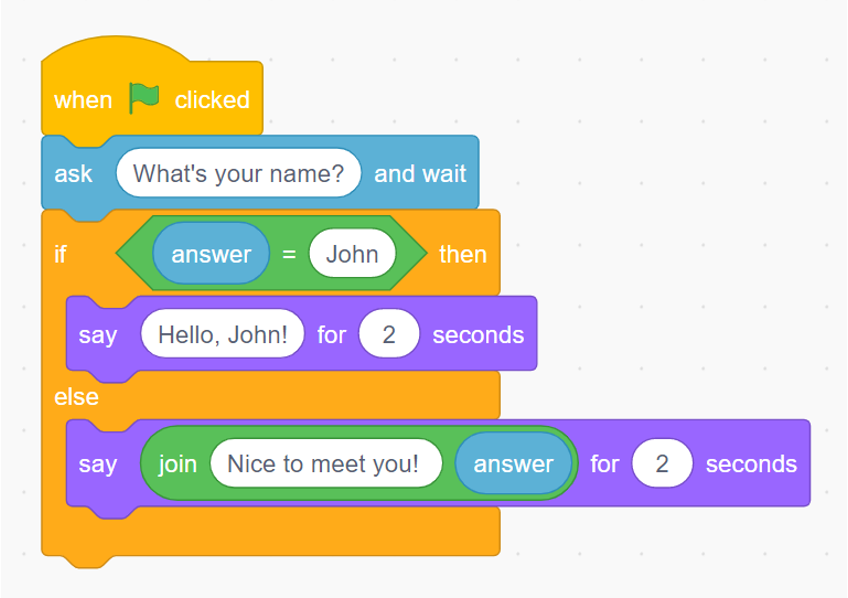
Condition is well known as an IF-Else statement which is decided what program should do. The choiced process is controled by the boolean condition that evaluates to be True or False.
# Iteration
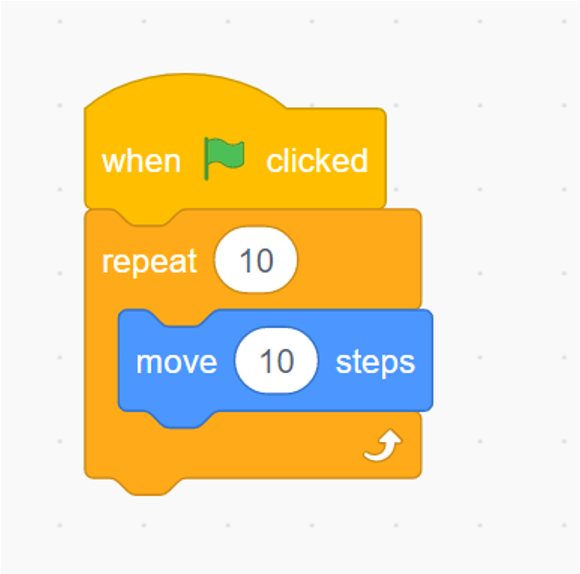
Iteration is also well known as a Loop. Basically, Iteration means we can repeat some statements which are related to the Sequence Control Flow. Moreover, Iteration can be controled by the boolean condition.
# What can we do with Python?
# Drawing and Animation
ankur1 = [
[0, 120],
...
[40, 120],
[0, 120],
]
ankur2 = [
[0, -30],
...
[40, -30],
[0, -30],
]
ankur3 = [
[0, -220],
...
[60, -220],
[0, -220],
]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20

...
while True:
moon.clear()
draw_moon(moon, "red", 100, 20)
draw_moon(crescent, "white", 100, 20)
move_moon(moon, 0.8)
screen.update()
...
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# Math Solving and Calculation
def fibonacci(n):
if n == 0:
return 0
if n == 1:
return 1
else:
return fibonacci(n-1) + fibonacci(n-2)
print(fibonacci(12))
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
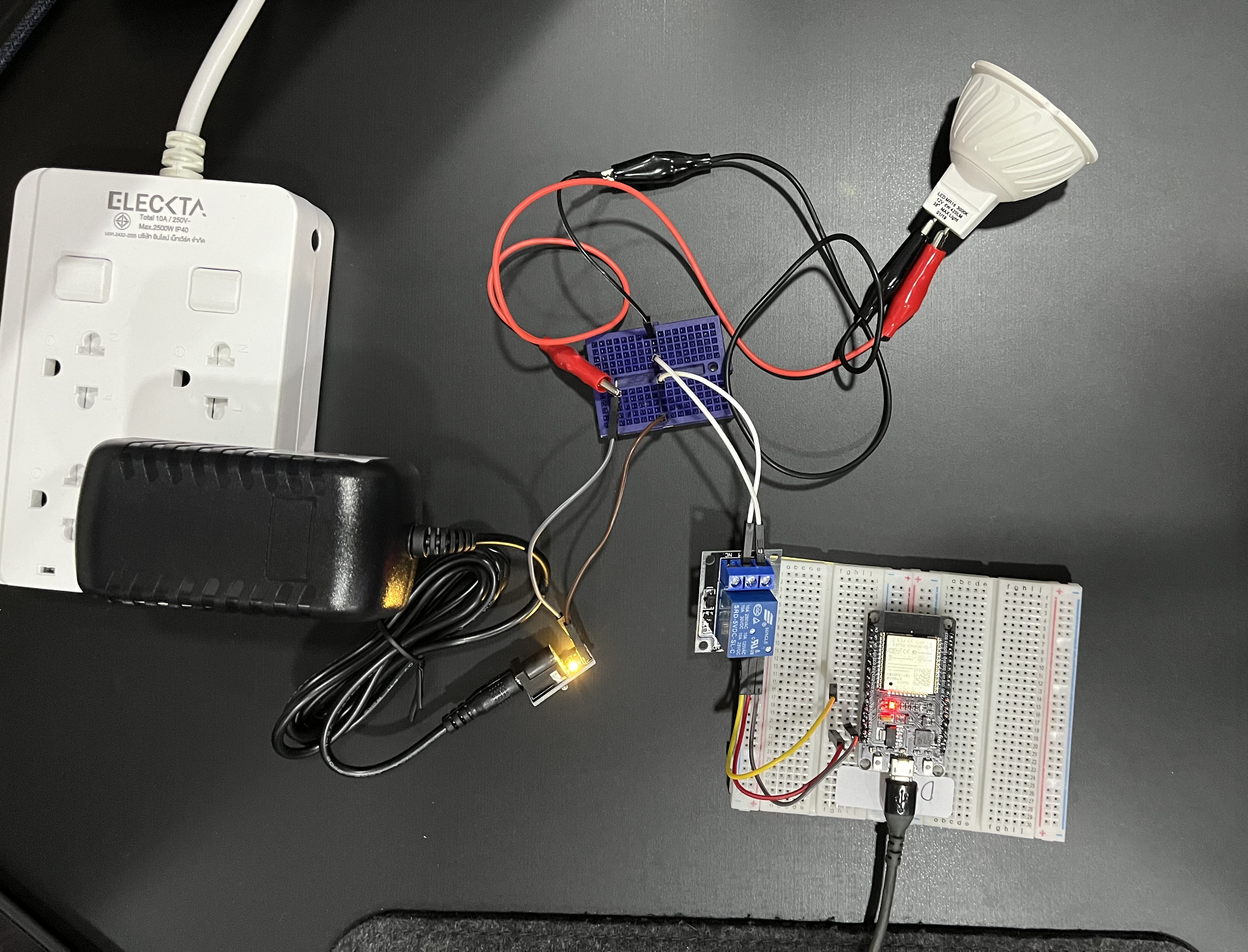
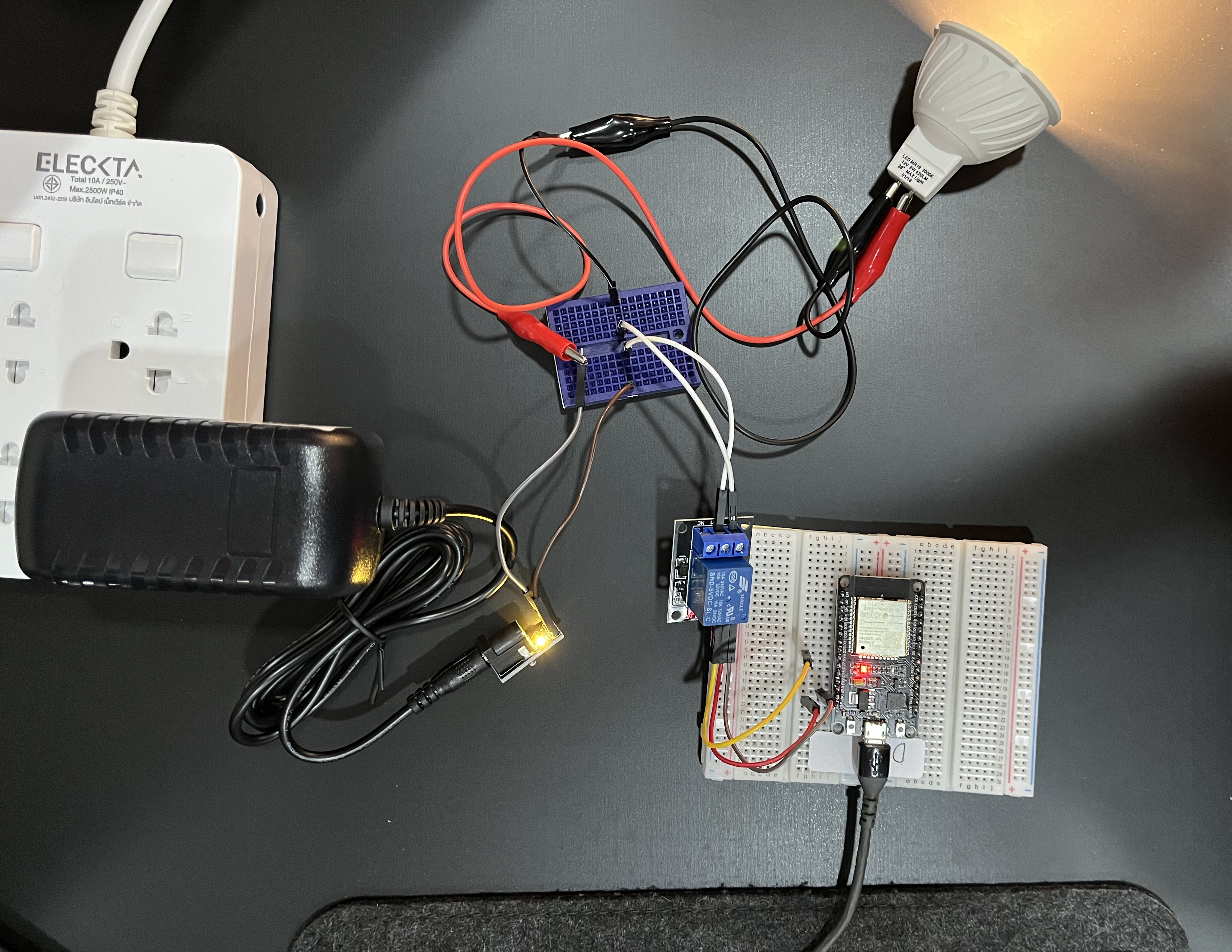
# Microcontroller
from machine import Pin
from utime import sleep
signal = Pin(26,Pin.OUT)
signal.off()
sleep(1)
signal.on()
sleep(1)
signal.off()
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# Data processing
Jessie=150
Zak=400
Chester=100
Jim=200
Chester=145
Alexander=200
...
Chester=100
Alexander=260
Zak=400
Chester=150
Jessie=170
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
employees = {}
salary_data = None
with open("salary.txt", "r") as salary_file:
salary_data = salary_file.readlines()
for each_record in salary_data:
split_data = each_record.split("=")
name = split_data[0]
money = float(split_data[1])
if name not in employees:
employees[name] = 0
employees[name] = employees[name] + money
print(employees)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
OUTPUT
{'Jessie': 1092.0, 'Zak': 2800.0,
'Chester': 1065.0, 'Jim': 1147.0,
'Alexander': 1670.0, 'Paul': 1025.0}
# Data Science and Data Analysis
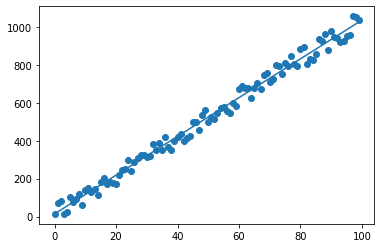
import numpy as np
def solve(x,y):
X = np.array(x).reshape(1,-1)
y = np.array(y).reshape(-1,1)
X = np.insert(X,0,np.ones(X.shape),axis=0)
X = X.T
c_m = ( np.dot( np.linalg.inv(np.dot(X.T,X)), np.dot(X.T, y) )).tolist()
print(f"m = {c_m[1][0]}")
print(f"c = {c_m[0][0]}")
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
import normal_equation
normal_equation.solve(month, number_students)
2
3
m = 10.223534353435346
c = 13.89504950495039
print(10.22*150 + 13.89)
OUTPUT
1546.89